Invoice report. Procedure and rules for preparing a product report. Product report “Movement in Excel”
Invoices are used to document transactions that affect the movement of goods and settlements with the counterparty.
To work with invoices, go to the block “Documents” - “Invoices” and select the required type of invoice. For more information on navigating through the list of primary documents, see the section.
Conditions and signs of invoices
In the columns of the list of accounts of any type, in addition to information about the account registered at the time of creation (for example, the date of registration of the account, its amount, etc.), columns of additional characteristics and states are displayed.
All incoming invoices (receipt invoices, return invoices from suppliers, acts of acceptance of goods for sale) have the following characteristics/conditions:
All outgoing invoices (invoices, sales reports, etc.) have the following states:
General characteristics of incoming and outgoing invoices:
Receipt and expense invoices
Receipt invoices reflect the receipt/receipt of goods from suppliers. Invoices reflect the shipment/transfer of goods to wholesale and small wholesale customers.
Registration of arrival/shipment of goods using an invoice
To register the receipt of goods using an invoice, follow these steps:

For the invoice:
- OZhPR- “waiting for arrival.” Set by default after creating an invoice. Increases the quantity of goods selected in the invoice specification in the columns “Oh. coming" in product lists in information cards and the “Nomenclature” directory.
- ODA- “the goods have been received.” Set this status to receive the goods. See more details. “Results of the operation” - “Movement of goods”.
- PGT- "Preparation". Set this state to not take into account information about the goods selected in the document specification (the quantity of goods specified in the specification will not affect the remaining goods, and the document amount will not appear in financial reports). For an invoice:
- RES- “reserve”. Set by default after creating an invoice. Increases the quantity of goods selected for the invoice specification in the “Reserve” columns in the lists of goods in information cards and the “Nomenclature” directory.
- OTG– “shipped.” Set this state to ship the item from the warehouse. For more details, see Operation results, Goods movement.
- PGT- "Preparation". Set this state to not take into account information about the goods selected in the document specification (the quantity of goods specified in the specification will not affect the remaining goods, and the document amount will not appear in financial reports).
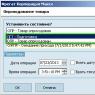
Select the required state and click "OK"- the invoice will appear in the list of invoices.
Results of the operation:
Movement of goods
Receipt invoice: after setting the status "Credited" the goods will be capitalized, which will cause an increase in the quantity of goods specified in the specification in the selected warehouse.
Invoice: after setting the status "Shipped" the goods will be shipped, which will cause a decrease in the quantity of goods specified in the specification in the selected warehouse.
You can check the movement of goods through warehouses in the following way:

Mutual settlements with the counterparty
Receipt/expenditure invoices are reflected in the report "Mutual settlements" after setting the state "capitalized"(for invoices) and "shipped"(for consumable invoices).
For more information about the report, see the section ["Reports", "Settlements"].
Note: The settings for possible product states described above are set by default. You can change state settings or create new ones in the [“Settings”] section ( Settings - Document settings - Receipt (expenditure) invoice - Document properties - States).
Creating an invoice based on an invoice
You can create an invoice based on an existing invoice in the system. This will allow you to fully or partially link the invoice amount with the receipt/shipment of goods. To create an invoice note, follow these steps:

Creating an invoice based on multiple invoices
It is possible to create an invoice for several accounts registered to the same counterparty. To do this, you need to mark the relevant accounts (see section) and follow the steps described in section.
Creating multiple invoices for one account
To create multiple invoices for one account, follow these steps:
- Repeat steps 1-2 described in section.
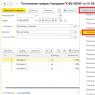
- To selectively enter items from an invoice, double-click on the item selected at the top of the window, then enter the quantity in the standard window "Product entry" and press the button "OK".
The specified quantity of goods will appear in the invoice specification.
To create another invoice based on the same invoice, repeat the steps above.
Each time you create a dependent document based on an invoice, the quantity of goods available for selection in the specification will be reduced by the quantity that was previously attached to other dependent documents.
Distribution of invoice goods according to customer orders
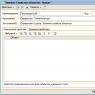
Use this function to automatically distribute goods on RECEIVING invoices to customer orders. To use the function, go to the list of receipts, right-click in the list area and select “Distribution of supplies according to customer orders” in the context menu:

Set the parameters for distributing invoice items among orders in the window that opens:
- Distribute
- All eligible receipts – goods from all receipt documents that are not tied to customer orders will be distributed according to customer orders.
- Selected documents – goods from only selected invoices will be distributed according to customer orders (pre-labeled invoices or an invoice on which the exchange rate was set at the time the function was called). - Period receipts only – check the box to select the period
- Only receipts from the supplier – only invoices with the selected supplier organization will be selected for distribution.
- Only for customer orders - selected products will be distributed only to the selected customer's orders.
- Only for trading organization -
- Post orders to supplier
- If the flag is not set, invoice goods will be distributed in chronological order, i.e. goods will be distributed first to customer orders registered on an earlier date.
- If the flag is set, invoice goods will be distributed first of all to those customer orders on the basis of which orders to suppliers were created.
After all the parameters have been set, click the “OK” button at the bottom of the window and wait until the operation is completed.
You can view the results of the operation in the section "Control of customer orders". As a result of the operation, changes will occur in the columns "Accepted to order", "Distributed to order", "Reserve". For more details, see “Control of customer orders”. Based on the results of the operation, reserve documents will be automatically created.
Supplier Returns/Customer Returns
Documents of this type are used to process returns to suppliers and returns from customers.
You can create an independent return document, as well as create a return document based on the invoice.
Create a new return label
To create a supplier return/customer return document, follow these steps:

Creating a return document based on an invoice
You can create a return invoice based on both the invoice and the invoice.
- Return to the supplier - based on the invoice.
- Return from the buyer - based on the invoice. To create a return document based on an invoice, follow these steps:
- Go to the list of incoming/outgoing invoices as described in the section.
- Find the required invoice in the invoice journal and select “Create a dependent document” - “Return invoice from the buyer”(for an invoice) or "Supplier return invoice"(for the invoice).
- On the tab "Goods"(see “Entering goods into the document specification”) an additional representation of goods will appear: according to the base document. On the tab "Maksim." displays the quantity of goods that were capitalized/written off when creating the basis document (receipt or expense invoice). The “Available” column displays the available quantity of the product, calculated according to the algorithm of the warehouse or return document. For more information about the calculation of the algorithm, see.
- Transfer the required products to the specification, as described in the section, and click "OK" in the return document creation window – the new return document will appear in the list.
If you try to write off a quantity of goods that exceeds the quantity indicated in the column "Maksim.", the program will generate an error.
Results of the operation:
Regarding the movement of goods and mutual settlements between counterparties, return documents function similarly to invoices.
A customer return works the same as a return slip. For more information about working with consumable invoices, see the section.
A return to supplier works in the same way as a delivery note. For more information about working with invoices, see the section.
Sales through the cash register/returns through the cash register
Documents of this type are generated AUTOMATICALLY
when registering sales/returns through the cash register program "Frigate POS".
Documents type "Sales through the cash register" are analogous to an invoice and affect the movement of goods and mutual settlements with the counterparty in the same way. For more information about working with consumable invoices, see the section.
Documents type "Returns at the checkout" are analogous to the invoice and affect the movement of goods and mutual settlements with the counterparty in the same way. For more information about working with invoices, see the section.
Acts of acceptance for implementation
Acts of acceptance for sale are used to accept goods for sale from partners.
To create an act of acceptance for sale, follow these steps:

Results of the operation:
As a result of creating an act of acceptance for sale, the goods will be posted to the selected warehouse, but there will be no mutual settlements with the counterparty, as when creating a regular invoice.
To register mutual settlements with the selling counterparty, follow these steps:
- Create an invoice as described in section. When creating an invoice, please note that the product must be selected from the receipts registered in the system as a result of creating acts of acceptance for sale. For more information on choosing goods by receipt, see section [""]
- Create an implementer report as described in the ["Implementer Reports"] section.
As a result of the described actions in the list of documents "Reports from implementers" documents will be created: commission agent reports, seller reports, agent reports - depending on the basis document. The amounts of these documents will be taken into account in mutual settlements. For more information about working with the report on mutual settlements with counterparties, see section [""]
Implementers' reports
Sellers' reports are generated automatically based on invoices, the specifications of which include goods from receipts registered using acts of acceptance for sale. To generate a report, follow these steps:

As a result, in the list of documents "Reports from implementers" documents will be created "Commissioner's Report", "Implementer's report", "Agent's Report"- depending on the basis document on the basis of which they were formed.
Acts of transfer for implementation
Acts of transfer for sale are used to control the quantity of goods transferred for sale to partners.
To create a transfer act for sale, follow these steps:
Follow steps 1-3 to create a document as described in section.
On the tab "Requisites" in field "Buyer" select the counterparty who is the seller. For more information on creating implementing organizations, see.
Setting the state of the transfer act for implementation
If necessary, you can set the status of the act of acceptance for implementation using the function "Set State". For more information about setting the state of documents, see the section.
Possible states of acts of acceptance for implementation coincide with the states of movement invoices. For more information about the status of movement invoices, see the section.
Results of the operation:
As a result of creating an act of transfer for sale, the goods selected in the document specification will be posted to the distributor's warehouse and written off from the warehouse of their organization. In this case, there will be no settlements with the seller.
To register the sale of goods specified in the act of transfer for sale, follow these steps:
- Create an invoice as described in section.
- On the tab "Requisites":
- in field "Salesman" select the selling organization specified in the transfer for sale act.
- in field "From the warehouse" indicate the distributor's warehouse (has the same name as the selling organization).
As a result of the described actions, an invoice will be created, the amount of which will be taken into account in mutual settlements with the selling counterparty. The quantity of goods entered into the specification of the invoice will be written off from the warehouse of the selling organization.
Deliveries/Shipments
Documents type "Supplies" And "Shipments" are used to establish relationships between several overheads and associated costs.
- Use the document "Supplies" ARRIVAL
- Use the document "Shipments" to establish communication between several CONSUMABLES overhead and a single cost.
To create a document "Supplies" or "Shipments", follow these steps:
Results of the operation
As a result of the described actions, an additional cost will be added to the list of costs of all invoices selected in the delivery/shipment document. This cost will not be available for editing in the list of costs for each invoice:
Information about business transactions carried out by an economic entity for a certain period of time is summarized in the relevant registers and from them is transferred in grouped form to the financial statements. In the system of regulatory regulation of accounting, financial statements are considered as a system of indicators reflecting the property and financial position of the organization as of the reporting date, as well as financial results for the reporting period. This procedure for summarizing accounting information is necessary, first of all, for the enterprise itself and is associated with the need to clarify, and in some cases, adjust the further course of its financial and economic activities. Therefore, financial statements must identify any facts, the content of which may affect users’ assessment of information about the state of property, financial situation, profits and losses.
Internal reporting is a system of interrelated economic indicators that characterizes the performance of departments over a certain period of time. Management reports are prepared at regular intervals. They cover all business processes: production, sales.
The financial statements of Kolos LLC include a profit and loss statement and a certificate of accounts payable.
The profit and loss statement (form No. 2) characterizes the financial results of the activities of Kolos LLC for the reporting period. (Appendix 2) The data in the report is presented in cumulative total from the beginning of the year to the reporting date (for 2004). At the same time, column 3 shows data for the reporting period, and column 4 - for the same period of the previous year. Negative exponents are written in parentheses.
General production expenses, as well as general business expenses, are reflected in the item “Administrative expenses”.
Costs associated with the sale of products are reflected in the item “Commercial expenses” of the income statement. Data for the item “Commercial expenses” shows the level of costs associated with the sale of products.
The certificate of accounts payable is presented for 2005. (Appendix 3) The certificate is drawn up for goods (work, services) accepted for accounting, including fixed assets, intangible assets, and property rights. It indicates the full name of the organizations, INNKPP, the number and date of the invoice, and the amount of accounts payable. Column 4 reflects the entire amount of debt, and column 5 shows the amount of VAT, calculated as well. At the end, the total amounts for both columns 4 and 5 are calculated.
Thus, the enterprise Kolos LLC has a debt in the amount of 61,478.17 thousand rubles, including VAT of 9197.34 thousand rubles.
In addition, the chief accountant of the company Kolos LLC conducts an analysis of general business expenses, an analysis of auxiliary production, the results of trade, an analysis of the work of the mill, and the final analysis is a general analysis of the work of Kolos LLC.
An analysis of general business expenses is provided for 2004-2005. and includes the following expenses: wages, deductions from wages, electricity, depreciation, fuels and lubricants, spare parts, stationery, communication services, corporate communications, building rental, Volga rental, travel allowances, water, heating and other expenses (bank service , newspaper subscriptions, cash register maintenance, labor protection, training, legal services). The deviations of the previous year compared to the base year are presented. As a result, general business expenses in 2005 amounted to 1223.5 thousand rubles, in 2004 - 1107.5 thousand rubles. those. expenses increased by 116 thousand rubles. due to increased wages, increased use of communication services and legal services, but decreased costs for the purchase of spare parts. (Appendix 4)
Analysis of auxiliary production for 2004-2005 shows the volume of services (revenue), wage costs, deductions from wages, depreciation, fuel and lubricants, spare parts, rent, travel, general business expenses and other expenses (vehicle repair, technical inspection, transport tax, labor protection). The costs of auxiliary production are 681 thousand. rub. in 2005 and 2004 - 604.1 thousand rub. And the volume of services in 2005 were produced for 659.8 thousand rubles, which is 21.2 thousand rubles. less than costs. (Appendix 5)
The results of the trade work of Kolos LLC are presented for 2004-2005. and for the 4th quarter of 2005. For 2004-2005. such indicators as trade turnover, gross income, costs, financial results, level of trade margins (in percentage), costs per 1 ruble are considered. turnover, UTII and financial result after tax. For the fourth quarter - turnover, realized overlays, profit from sales, number of sellers, average salary of sellers. The results are carried out by stores: Khlebushko-1 and Khlebushko-2, and the latter is divided into retail and other sales. In 2005, the trade of Kolos LLC had a profit of 110.1 thousand. rub., which is 90.8 thousand rubles. more compared to 2004 (Appendix 6 and 7)
The mill operation analysis was compiled for 2004-2005. Contains the same indicators as the analysis of auxiliary production. Only other expenses include a large number of costs, because The mill is the main activity of the Kolos LLC enterprise. Analyzing the operation of the mill, we can say that in 2005, revenue increased by 1063.2 thousand rubles compared to 2004, but operating costs also increased by 1343.1 thousand. rub. Total expenses in 2005 amounted to 6886.9 thousand rubles, including other expenses of 162 thousand rubles. (ecology, maintenance of special automation, equipment, repair of scales, garbage removal, etc.). The financial result shows that the company is incurring losses, because in 2005 it was equal to -2896.3 thousand rubles. (profit = revenue - cost = 3990.6 thousand rubles - 6886.9 thousand rubles). (Appendix 8)
At the end of the year, based on the above analyses, the chief accountant of the enterprise Kolos LLC makes a general analysis. This analysis summarizes all types of activities of the organization: mill, auxiliary production, wholesale and retail trade. Such indicators as revenue, cost and financial results are considered. Revenue increased by 4850.3 thousand rubles. Growth occurred in all types of activities and, especially in retail trade. The cost of the enterprise also increased by 4962.1 thousand rubles. In general, the company Kolos LLC is incurring losses due to activities such as mills and auxiliary production; they need to be reduced. Trading activities, mainly retail, are profitable. Therefore, the Kolos LLC enterprise must develop this type of activity by expanding retail space, improving the quality of service and meeting the demand of the population. (Appendix 9)
Thus, reports on overhead costs allow the company Kolos LLC:
distribute responsibility for overhead costs;
distribute overhead costs between activities;
develop measures to reduce overhead costs based on information about cost carriers (cost carriers are reduced and overhead costs are reduced);
prepare information for making management decisions;
conduct an analysis of variances in overhead costs depending on the factors influencing them;
carry out operational management of deviations.
Description of new forms.
Many of the forms from this distribution use new internal language constructs, so they can be used with program version 5.3.2 and higher, preferably 5.4.2.
Some reports require MS Excel installed. Interaction with Excel occurs using the OLE Automation mechanism. Excel report templates are located in the database folder. When generating reports, copies of these files are created, so to edit the report form in Excel, you need to open the template in the folder with the database.
1. Report on invoices “Excel: invoices and profit”
"Excel: invoices and profit" available when selecting the menu “Reports – Sales of goods – By invoices”, as well as in the “Retail” section in the list of sales invoices, the “Reports” button.The report in an Excel table displays a list of invoices for the release of goods with the amount of the invoice and the profit received from the invoice. The total amount of shipment and the amount of profit are calculated.
To calculate profits, before receiving the report, you must make a CALCULATION OF THE MOVEMENT OF GOODS.
2. Report on goods “Movement in Excel”
"Motion in Excel" can be obtained by selecting the menu “Reports – General – By goods and receipt/issue from warehouse”. It replaces a similar report that already came with the program.For each product, balances and costs at the beginning and end of the period, the volume of supplies and sales for the period, and the profit received are calculated. It is possible to detail operations on invoices.
This report is an alternative to reports received after calculating the movement of goods, for example, “01 Movement. goods - universal report (required calculation)”, if you need details of the movement of invoices.

3. “Excel: Inventory balances” report
"Excel: Remaining goods" can be obtained by selecting the menu “Reports – General – By goods and receipt/issue from warehouse”. The report allows you to obtain stock balances at the current moment or on an arbitrary date. The amount of balances can be calculated at cost or at one of the selling prices. Similar reports have long been supplied with the program, but they are mostly in text format.
4. Reports “Transactions with clients (detailed)” and “Retail transactions with clients (detailed)”
"Operations with clients (details)" And "Retail operations with customers (in detail)" are found in general customer reports and in reports in the “Retail” section. For each client, information about shipments is displayed indicating the product name, quantity and price. A similar report was previously supplied, but it was not in the “Retail” section.5. Report “Detailed account report 2”
“Detailed account report 2” found in sales order reports. It displays detailed information on orders indicating the list of ordered goods. This report is a revised version of a report that has long been supplied with the program.6. Reports “Transaction amounts and profit by day”
Two reports in Excel format “Transaction amounts and profit by day” are located in general reports on invoices and in reports on invoices in the “Retail” section. They allow you to get the dynamics of operations and profits. For each day, the amount of purchases, the amount of returns to suppliers, the amount of sales, the amount of returns from customers, and profit are calculated. This data can be used to create charts and graphs.

7. Form of the waybill
Form waybill in Excel format has been added to the section “Sale of goods – Preparation of invoices for orders”. The form is located on two sheets of an Excel workbook. The first sheet contains the product part, the second - the transport part.
The third sheet contains a list of drivers, data from which can be used in the transport part. It should be noted that when generating a document, a copy of the original TRANSP.XLS file is opened, which is located in the folder with the database. To specify a list of drivers, you need to edit this file.
To make it easier to enter the transport part of the invoice, there is a button “Enter the transport part”. When you click it, a form appears for filling out the transport part data.

– this invoice form in Excel format has been added to the “Sale of goods – Preparation of invoices for orders” section. It displays the country of origin and the customs declaration number for the goods. This form can be used as a waybill.

9. Reports “Payment reconciliation with Excel table”
“Reconciliation of payments with Excel table” are found in the reports for cash payments and payments by payment order in the sales section.These forms are convenient to use to reconcile payments entered into the program with a list of payments in an Excel spreadsheet. The Excel file may contain data obtained from a client-bank program or an accounting program.
At enterprises involved in the trade sector, a commodity report in the TORG 29 form is used.
This form is ideal for those who use the balance method of accounting for goods.
Who should compile it? What rules need to be taken into account when filling out this form? How often is it submitted to the accounting department? Here you will find answers and tips to all these questions.
The concept of a product report. Legislative framework for this issue
The use of the standard interindustry form N TORG-29 (“Commodity Report”) is recommended by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation for enterprises whose activities are related to retail trade services.
 By this body on December 25, 1998. instructions were given to fill out such forms with detailed justification in Resolution No. 132 “On approval of unified forms for recording trade transactions.”
By this body on December 25, 1998. instructions were given to fill out such forms with detailed justification in Resolution No. 132 “On approval of unified forms for recording trade transactions.”
The standard form is used for reporting by responsible persons in order to control documentation on trade turnover for certain periods of time. The form is designed in such a way that it is necessary to reflect the data of invoices, indicating the date of their preparation and the total amounts. At the end of the report, the general results of financial transactions during the movement of goods are indicated, as well as their balance in monetary equivalent at the end of the month.
Application and purpose
 In any organization where the movement of goods takes place, it is imperative to register their receipt and decrease. For this purpose, in accounting, documentation of the receipt and release of goods is formed in special registers.
In any organization where the movement of goods takes place, it is imperative to register their receipt and decrease. For this purpose, in accounting, documentation of the receipt and release of goods is formed in special registers.
Reconciliation of balances and the reliability of the availability of shipping documentation is carried out on the basis of commodity reports submitted to the accounting department in the TORG 29 form. In it, the reporting employee summarizes all the information on the papers about the arrival and departure of his commodity mass. Thus, the report is, in its own way, a register of invoices, compiled into separate lists according to the documents received. By amounts reflected final figures are calculated separately about the amount of goods arrived and lost, as well as their balance at the beginning and end of the reporting period.
This form of report easily allows you to control the turnover of a separate area for which the responsible person is responsible. The main thing in this matter is not to make mistakes and carefully fill out the form, then everything will be in order at the enterprise.
If you have not yet registered an organization, then easiest way This can be done using online services that will help you generate all the necessary documents for free: If you already have an organization and you are thinking about how to simplify and automate accounting and reporting, then the following online services will come to the rescue and will completely replace an accountant at your enterprise and will save a lot of money and time. All reporting is generated automatically, signed electronically and sent automatically online. It is ideal for individual entrepreneurs or LLCs on the simplified tax system, UTII, PSN, TS, OSNO.
Everything happens in a few clicks, without queues and stress. Try it and you will be surprised how easy it has become!
Registration procedure
For convenience, this report is used in companies engaged in the sale of goods at retail, and accounting of activities upon their receipt and departure is carried out using the sales price. Convenient for those enterprises that use the cost method of accounting for goods, called the balance method.
Requirements to this document are:
- How many copies are made? It's served in duplicate, one of which remains in the accounting department with the original documents attached to it, and the second remains with the responsible person.
- Which employees should report? The duty to draw it up refers to those who receive and issue goods. This employee submits the report to the accountant for verification. If everything is in order, then one copy of the two forms is endorsed by the inspector and returned to the responsible person.
- How is data entered into the report? Filling in parameters from the turnover documentation received during the reporting period, done both electronically and manually using a pen with blue or black ink.
- What should this document confirm? All information reflected in the TORG 29 form is confirmation of goods movement: how much has arrived and left, as well as what balance is available at the end of the reporting period.
- Grounds and procedure for using the TORG 29 form. Fill out the form financially responsible person, based on the availability of documents for the reporting period, approved by the chief manager of the organization. All documents are divided into 2 tables about the receipt and consumption of goods in accordance with the chronological order of their creation.
- Storage each copy of completed TORG 29 forms. One of them is kept in the archives of the accounting department of the trade organization, and the other is kept by the financially responsible person.
Now let's move on to filling out the report form itself.


Filling rules
The following will help you fill out the report: step-by-step instruction:
- Product report forms are filled out and submitted within the period specified by the manager, which cannot be more than 10 days. It is possible to prepare a report twice during the reporting period approved by management, for example, when conducting an inventory.
- The document must be drawn up in 2 copies by the financially responsible employee who is entrusted with the management and storage of the products sold.
- All product reports must be numbered consecutively, starting from the beginning of the year. An exception is the case when a new materially responsible person is appointed. In such circumstances, the numbering begins anew from the moment he takes office.
- The most often used is a unified form for a commodity report under No. TORG-29, consisting of two pages separately for incoming and outgoing papers. In chronological order, each document is recorded in a separate line, first from the receipt documents, and on the next page, in the same order, the consumables are recorded.
- Before you start entering data from invoices and cash (and) orders, you need to fill out the information in the header of the form. In this part, you must enter the full name of the organization, for example, “Limited Liability Company “Alexandria”. Below you enter data about the structural unit, for example, a warehouse.
- After information about the organization and department or site, enter information about the materially responsible person: his individual data, position, personnel number.
- Start filling out the table from where you indicate the balance at the beginning of the check. The balance at the beginning of the period must be the same as the balance at the end of the previous product report form. Then enter line by line in chronological order the data from receipt documents and invoices: name, date, number, amount of goods, cost of packaging.
note that all parameters of each document are entered separately. Even if invoices are from the same supplier and goods are delivered on the same day, they cannot be summed up. After filling out all receipt documents, the total receipt amounts for the reporting period are displayed at the end. - We move on to the next stage of reporting: fill out page two, in which you need to reflect all the information about the expense. The tabular data in the expenditure form is filled out in the same way as the receipt register of documents on the first sheet. At the end, the total expense amounts are indicated.
Note! Don’t forget to also include information about goods returned to suppliers in your expense list. - They finish filling out the form by indicating in the “Appendix” section the number of shipping papers and in the indicated place the financially responsible person puts his signature.
- The completed TORG 29 form is submitted to the accounting department, where it is checked immediately on the day of submission. If the report coincides with the accounting data, then after reconciling them, the accountant must put his marks in columns 6 and 7, as well as his signature.
Making corrections
When filling out the report electronically, errors can be easily corrected. But if the form is filled out manually, then it is rarely possible to avoid errors when compiling it. However, corrections may be made to the report.
 If an error is found, it can be corrected. To do this, inaccurate information is crossed out with one line, and the correct entry is made above it.
If an error is found, it can be corrected. To do this, inaccurate information is crossed out with one line, and the correct entry is made above it.
Near the fix enter such data:
- who made the adjustments;
- calendar number of corrections made;
- signature of the person who entered the correct data.
In a report, it is unacceptable to cover up incorrect parameters with a corrector or shade them with several lines.
If there are a lot of errors in the report, then it must be completely rewritten on a new form.
Accounting and storage
This type of reporting is subject to the rules of documentation when accepting, storing and distributing commercial products, as well as posting completed turnover transactions in accounting.
To correctly fill out and use the forms, you must use the Methodological Recommendations for recording transactions with goods in the trade sector, approved by letter N 1-794/32-5 of Roskomtorg dated July 10, 1996.
So, based on these regulations, product reports, together with the documents attached to them, are collected in a binder sequentially according to their serial numbers. Their storage period is 5 years. The main responsibility for ensuring the safety of such documentation rests with the chief accountant.
Responsibility for the absence of these reports
Taxpayers will have to answer for the lack of reporting documentation under Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This fact is a case of gross violations of the points specified in the rules for accounting for income and expenses when taxing organizations.
 The law stipulates that the employee appointed responsible for recording the facts of the economic life of a retail facility is obliged to ensure the issuance of primary documentation for the timely entry of data into accounting.
The law stipulates that the employee appointed responsible for recording the facts of the economic life of a retail facility is obliged to ensure the issuance of primary documentation for the timely entry of data into accounting.
But punishment can be incurred only for the following violations:
- errors made due to failure to comply with accounting rules;
- late submission of reports to the accounting department;
- failure to comply with the procedure or failure to maintain the established period for storing accounting documentation.
Only persons holding responsible positions in the organization are subject to punishment. This is described in Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Please note that the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not provide for punishment for the absence of primary documentation.
The rules for preparing a product report in 1C are outlined in the following video instructions: